On this page
Non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) CO2 sensors are widely used in various industries for measuring carbon dioxide levels with high accuracy and reliability. Whether in environmental monitoring, HVAC systems, or industrial applications, these sensors offer a dependable solution for CO2 detection. In this article, we'll explore how NDIR CO2 sensors work, breaking down the key principles and components that enable them to function effectively.
The operation of an NDIR CO2 sensor is based on the principle of infrared light absorption. Each gas absorbs light at specific wavelengths, and carbon dioxide (CO2) is known to absorb infrared light at a wavelength of around 4.26 micrometers. In an NDIR sensor, an infrared light source emits light through a sample of air or gas, and a detector measures how much of that light is absorbed by CO2 molecules. The difference between the emitted light and the absorbed light allows the sensor to calculate the concentration of CO2 in the air.
What makes NDIR sensors "non-dispersive" is that they do not disperse light into its component wavelengths (like a spectrometer does); instead, they focus on a specific wavelength that is absorbed by CO2, making the measurement process more straightforward and efficient. To better understand how NDIR CO2 sensors work, let's look at the main components that contribute to their operation: The infrared (IR) light source is a crucial component of the sensor, emitting infrared radiation that passes through the gas sample. This light typically has a broad spectrum that includes the wavelength absorbed by CO2. The light source is designed to be stable and long-lasting, ensuring reliable performance over time. The detector is responsible for measuring the amount of infrared light that passes through the gas sample and reaches the other side of the sensor. By comparing the intensity of the light before and after it passes through the gas, the detector can calculate how much light was absorbed by the CO2 molecules, which correlates to the CO2 concentration in the sample. The optical path is the space through which the infrared light travels between the light source and the detector. This path is often designed to optimize the interaction between the light and the gas molecules, ensuring that enough CO2 absorbs the infrared light to produce an accurate measurement. A mechanical chopper is a rotating device that periodically interrupts the infrared light beam, enabling the sensor to differentiate between ambient infrared radiation and the IR light emitted by the sensor's source. This improves the accuracy and reliability of the measurement by reducing interference from external light sources. The raw data collected by the detector must be processed to provide a readable CO2 concentration. This is done by the sensor’s signal processing and electronics components, which convert the detector's output into a meaningful measurement. These components handle the calibration, filtering, and output of the final CO2 readings. The process by which an NDIR CO2 sensor works can be broken down into several key steps: The IR light source emits infrared radiation, which passes through a chamber containing the air or gas sample. As the infrared light travels through the gas, CO2 molecules absorb specific wavelengths of the light, particularly around the 4.26-micrometer range. The more CO2 in the air, the more light is absorbed. The detector on the opposite side of the gas chamber measures the amount of infrared light that reaches it after passing through the gas. The difference in light intensity before and after the gas interaction helps determine how much CO2 is present. The sensor's electronics process the data from the detector, compensating for any noise or interference, and converts the absorption data into a CO2 concentration reading. Calibration data is also factored in during this process to ensure accuracy.
This entire process happens in real-time, allowing NDIR CO2 sensors to provide continuous and accurate monitoring of carbon dioxide levels.
What makes NDIR sensors "non-dispersive" is that they do not disperse light into its component wavelengths (like a spectrometer does); instead, they focus on a specific wavelength that is absorbed by CO2, making the measurement process more straightforward and efficient. To better understand how NDIR CO2 sensors work, let's look at the main components that contribute to their operation: The infrared (IR) light source is a crucial component of the sensor, emitting infrared radiation that passes through the gas sample. This light typically has a broad spectrum that includes the wavelength absorbed by CO2. The light source is designed to be stable and long-lasting, ensuring reliable performance over time. The detector is responsible for measuring the amount of infrared light that passes through the gas sample and reaches the other side of the sensor. By comparing the intensity of the light before and after it passes through the gas, the detector can calculate how much light was absorbed by the CO2 molecules, which correlates to the CO2 concentration in the sample. The optical path is the space through which the infrared light travels between the light source and the detector. This path is often designed to optimize the interaction between the light and the gas molecules, ensuring that enough CO2 absorbs the infrared light to produce an accurate measurement. A mechanical chopper is a rotating device that periodically interrupts the infrared light beam, enabling the sensor to differentiate between ambient infrared radiation and the IR light emitted by the sensor's source. This improves the accuracy and reliability of the measurement by reducing interference from external light sources. The raw data collected by the detector must be processed to provide a readable CO2 concentration. This is done by the sensor’s signal processing and electronics components, which convert the detector's output into a meaningful measurement. These components handle the calibration, filtering, and output of the final CO2 readings. The process by which an NDIR CO2 sensor works can be broken down into several key steps: The IR light source emits infrared radiation, which passes through a chamber containing the air or gas sample. As the infrared light travels through the gas, CO2 molecules absorb specific wavelengths of the light, particularly around the 4.26-micrometer range. The more CO2 in the air, the more light is absorbed. The detector on the opposite side of the gas chamber measures the amount of infrared light that reaches it after passing through the gas. The difference in light intensity before and after the gas interaction helps determine how much CO2 is present. The sensor's electronics process the data from the detector, compensating for any noise or interference, and converts the absorption data into a CO2 concentration reading. Calibration data is also factored in during this process to ensure accuracy.
This entire process happens in real-time, allowing NDIR CO2 sensors to provide continuous and accurate monitoring of carbon dioxide levels.
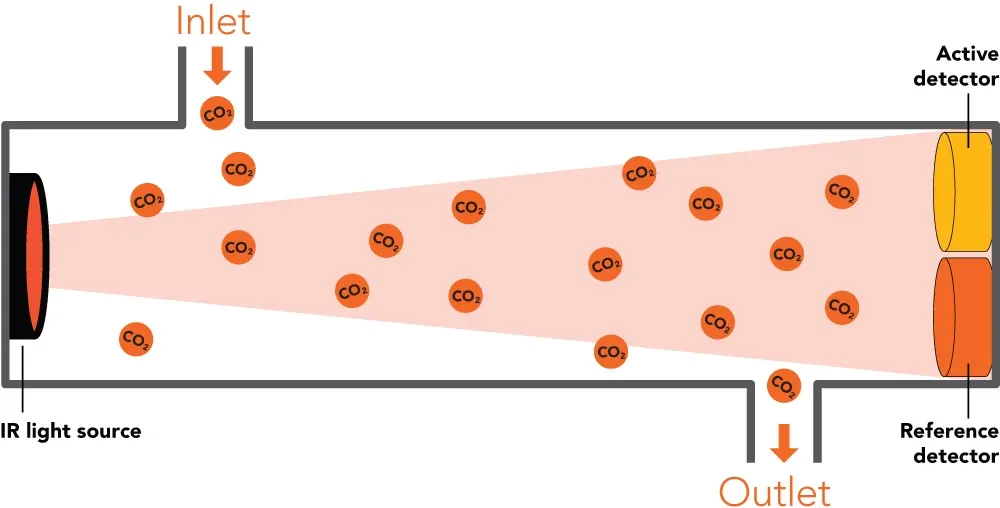
Understanding how NDIR CO2 sensors work and their components enables better utilization of these versatile tools in real-world applications. Whether in environmental monitoring or industrial safety, NDIR CO2 sensors play a critical role in maintaining a safe and healthy atmosphere.
Previous: Air Quality Sensor: Ensuring a Healthier Environment
Next: Monitoring the Environment: The Importance of Air Quality Sensors




