To verify the advantages of the proposed system detector in terms of efficiency, accuracy and comprehensive error of sensors, a simulation comparison experiment was carried out, and a comprehensive comparison was made between the intelligent sensors and the traditional sensor based on electrochemical methods and weighing methods. First, based on the three designs, 10 groups of comparative experiments were carried out under different degrees of air pollution, and the detection efficiency of various detectors was analyzed. The extracted statistical data are shown in Table 1: From the statistics in Table 1, it can be concluded that when the external air pollution is serious, the detection efficiencies of the three detectors are similar, and when the pollution is not serious, the efficiency of the system design is the highest.
Table 1 A comparison of the efficiency of detection of PM2.5 particles
Table 1 A comparison of the efficiency of detection of PM2.5 particles
| Pollution levels | Electrochemical detectors | Gravimetric detectors | The intelligent detector proposed in this article |
| I | 1.23 | 1.59 | 0.92 |
| II | 1.20 | 1.54 | 0.90 |
| III | 1.18 | 1.24 | 0 87 |
| IV | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.82 |
| V | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.80 |
| VI | 0.85 | 0.90 | 0.81 |
| VII | 0.76 | 0.80 | 0.70 |
| VIII | 0.69 | 0.79 | 0.68 |
| IX | 0.53 | 0.62 | 0.52 |
| X | 0.41 | 0.52 | 0.42 |
To verify the effectiveness of the accuracy of the detection, the data performance of the three detectors in terms of detection accuracy was also counted under 10 different levels of pollution, as shown in Table 2. The data changes in Table 2 show that the change in the detection accuracy of the electrochemical detector is positively correlated with the degree of air pollution; while the detection accuracy of the gravimetric detector is poor under the condition of light pollution. With the increase in the concentration of PM2.5 particles, the detection accuracy has improved; the detection accuracy for the intelligent sensor is stable, and the average detection rate can reach 97.84% in each pollution base, while those of the electrochemical detector and the gravimetric detector only reach 93.30% and 91.16%.
Table 2 Accuracy of detection of PM2.5 Particles
| Pollution levels | Electrochemical detectors | Gravimetric detectors | Intelligent detectors |
| I | 92.35 | 88.96 | 97.36 |
| II | 91.32 | 86.20 | 97.39 |
| III | 92.80 | 87.65 | 97.69 |
| IV | 92.81 | 89.25 | 98.01 |
| V | 93.02 | 89.31 | 96.97 |
| VI | 93.25 | 91.36 | 98.09 |
| VII | 93.65 | 92.54 | 97.63 |
| VIII | 94.30 | 94.53 | 98.54 |
| IX | 94.57 | 95.48 | 98.71 |
| X | 94.88 | 96.31 | 97.96 |
| Average values | 93.30 | 91.16 | 97.84 |
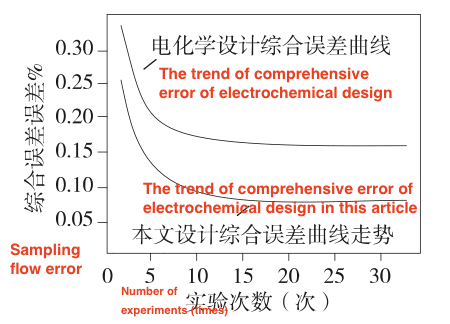
Figure 4 A comparison of sampling flow error of two methods
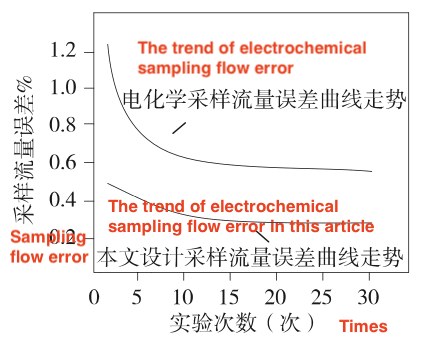
Figure 5 A comparison of comprehensive error of PM2.5 particle detection by two methods
Finally, the sampling flow error designed and the comprehensive error of PM2.5 particle detection were compared with the electrochemical detector. The curve changes in the statistical results are shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5.
It can be seen from the curve changes in the above figure that the control of the two errors of the intelligent sensor is better than that of the traditional sensor. The sampling flow error can be controlled below 0.5%, and the comprehensive error of PM2.5 particle detection is below 0.25%. Experimental data show that the detector proposed in this article has good performance in detection efficiency, precision and error control method.
3. Conclusion
With the advancement of industrialization and the rapid increase in the number of motor vehicles in recent years, air pollution in some areas tends to become serious, and the problem of smog has become a social problem. To deal with smog, it is still necessary to focus on prevention. A portable intelligent PM2.5 detector based on a laser dust sensor is proposed. The experimental results show that the proposed detector has better detection results under different pollution levels, and it has a small volume and is easy to use.
Previous: Intelligent PM2.5 Sensors
Next: Atmospheric Particles




