1. Using infrared light scattering to measure the concentration of dust
At present, there are many methods for measuring the concentration of dust at home and abroad, and the measurement methods can be divided into weighing, light scattering, β-ray and micro-oscillating balance. Among these methods, light scattering has the advantages of fast detection speed, good repeatability, and timely data processing, and is widely used in detecting the concentration of dust.
Light scattering refers to the phenomenon that the optical fiber deviates from its original propagation direction and spreads to all directions through an inhomogeneous medium. Dust particles will produce scattered light when they are irradiated by light. The scattered light signal is strong when the particle is large, and the scattered light intensity is proportional to the particle size.
When the light passes through the medium, it will interact with the medium. In addition to being scattered by the medium, it will also be absorbed by the medium. The absorption relationship conforms to Lambert-Beer's law of infrared absorption. When parallel light passes through a homogeneous medium, the concentration of dust is calculated by measuring the incident light intensity and outgoing light intensity based on Lambert Beer's law.
2. Detecting particles with small sizes
In people's daily life, some indoor pollutants with small particle sizes will be produced. Traditional infrared dust detection can only detect particles above 1μm, and only uses heating resistors to drive the sampling airflow. The number of samples is small, and the data calculation is completely handed over to the upper computer, so the measurement accuracy is relatively insufficient.
(1) Detection of small particle size particles by infrared light scattering method
With the deepening of research on the infrared light sources and sensor technology, the infrared dust sensor is improved and upgraded, and infrared dust detection is developed, which can accurately detect particles of small sizes.
The infrared dust sensor is developed based on the core sensing technology with independent intellectual property rights. PM1006 adopts the principle of optical scattering. The sensor has a built-in infrared light-emitting diode, a photosensitive tube and two condenser lenses. The light concentration effect of the lens is used to enhance the light intensity of the LED emitted light and the scattered light after encountering dust, so that it can accurately detect the variation trend of particle concentration in the indoor air with particle size between 0.3μm and 10μm.
(2) Features of PM1006
The shell of the infrared dust sensor module PM1006 is designed with an electromagnetic shield, integrated temperature compensation and dust accumulation compensation algorithm, which can effectively reduce the impact of the external environment on the detection results, with high detection accuracy and good sensitivity. The optical pulse working mode is used to improve the accuracy of the original signal, improving the signal-to-noise ratio of the original signal and reducing power consumption by lower than 30mA.
① Infrared LED light source
According to the principle of light scattering, the light emitted by the infrared LED is converged by the lens and then encounters dust to generate scattered light. After the scattered light is converged by the lens, it is recognized by the photosensitive detector and converted into an electrical signal. After the electrical signal is processed by the MCU, it will be converted into a signal to output the concentration of dust. When no dust is detected, the photosensitive detector outputs a low pulse; when the dust is detected, it outputs a high pulse, and the pulse signal is proportional to the detected light intensity.
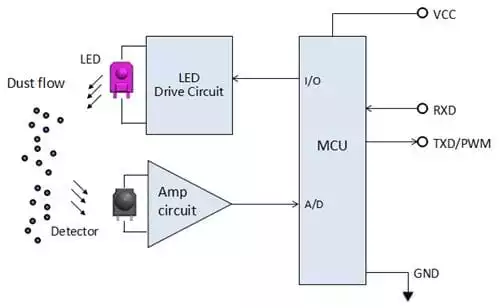
Figure 2 The working principle of infrared LED light source
② Communication protocol
The infrared dust sensor can collect the value of the on-site concentration of dust in real time, and has two communication outputs of UART and PWM, which can meet the requirements of the concentration of dust monitoring system. The effective potential of the infrared dust sensor is low-level effective, and the potential judgment method of PM1006 is 4ms potential judgment. Its advantages are as follows:
• When the sensor keeps outputting a low level, the client can judge that the current test value of the sensor is 992ug/m3 through the high level of 4ms, rather than failure in the client device.
• When the sensor keeps outputting a high level, the client can judge that the current test value of the sensor is 0ug/m3 through the low level of 4ms, rather than failure in the client device.
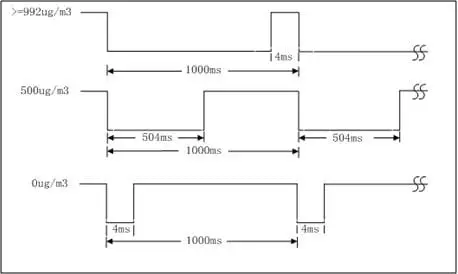
Figure 3 PM1006 PWM communication protocol
③ Consistency and accuracy of detection under normal temperature environment
To verify the dust detection performance of the infrared dust sensor module PM1006, it is used to test 8mg of Hongtashan at an ambient temperature of 25±2°C and an ambient humidity of 50±10%RH. The test results show that the actual error of consistency error of PM1006 at room temperature is ±10%, and the accuracy error at room temperature meets the reading ±20ug/m3 or ±20%. Compared with ordinary infrared dust sensors, it has better consistency and accuracy.
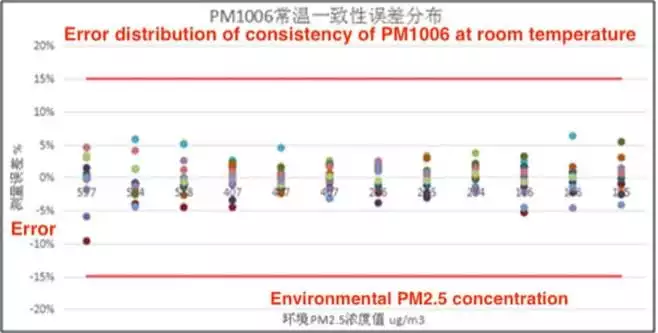
Figure 4 Error Distribution of Normal Temperature Consistency of PM1006
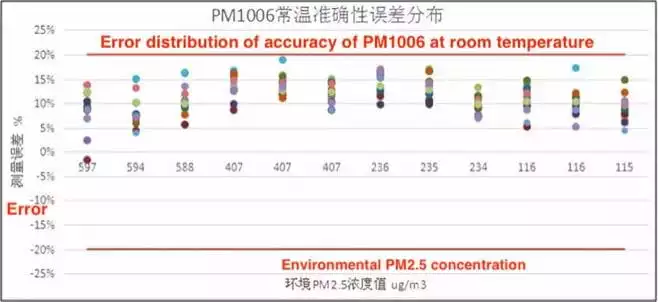
Figure 5 Error distribution of room temperature accuracy of PM1006
4. Conclusion
Infrared dust sensor PM1006 has small sizes and low costs, and can be embedded in other household appliances or equipment that need to monitor air quality in real time, such as household air purifiers, air quality detectors, fresh air systems, air conditioners with purification functions, and accessories of consumer electronics, providing control signals for these instruments. The concentration of air dust in the environment can be calculated through the output of the infrared dust sensor. When the detected dust concentration is higher or lower than the set dust concentration threshold, the device is turned on or off to achieve the purpose of controlling the indoor concentration of dust.
Light scattering refers to the phenomenon that the optical fiber deviates from its original propagation direction and spreads to all directions through an inhomogeneous medium. Dust particles will produce scattered light when they are irradiated by light. The scattered light signal is strong when the particle is large, and the scattered light intensity is proportional to the particle size.
When the light passes through the medium, it will interact with the medium. In addition to being scattered by the medium, it will also be absorbed by the medium. The absorption relationship conforms to Lambert-Beer's law of infrared absorption. When parallel light passes through a homogeneous medium, the concentration of dust is calculated by measuring the incident light intensity and outgoing light intensity based on Lambert Beer's law.
2. Detecting particles with small sizes
In people's daily life, some indoor pollutants with small particle sizes will be produced. Traditional infrared dust detection can only detect particles above 1μm, and only uses heating resistors to drive the sampling airflow. The number of samples is small, and the data calculation is completely handed over to the upper computer, so the measurement accuracy is relatively insufficient.
(1) Detection of small particle size particles by infrared light scattering method
With the deepening of research on the infrared light sources and sensor technology, the infrared dust sensor is improved and upgraded, and infrared dust detection is developed, which can accurately detect particles of small sizes.
The infrared dust sensor is developed based on the core sensing technology with independent intellectual property rights. PM1006 adopts the principle of optical scattering. The sensor has a built-in infrared light-emitting diode, a photosensitive tube and two condenser lenses. The light concentration effect of the lens is used to enhance the light intensity of the LED emitted light and the scattered light after encountering dust, so that it can accurately detect the variation trend of particle concentration in the indoor air with particle size between 0.3μm and 10μm.
(2) Features of PM1006
The shell of the infrared dust sensor module PM1006 is designed with an electromagnetic shield, integrated temperature compensation and dust accumulation compensation algorithm, which can effectively reduce the impact of the external environment on the detection results, with high detection accuracy and good sensitivity. The optical pulse working mode is used to improve the accuracy of the original signal, improving the signal-to-noise ratio of the original signal and reducing power consumption by lower than 30mA.
① Infrared LED light source
According to the principle of light scattering, the light emitted by the infrared LED is converged by the lens and then encounters dust to generate scattered light. After the scattered light is converged by the lens, it is recognized by the photosensitive detector and converted into an electrical signal. After the electrical signal is processed by the MCU, it will be converted into a signal to output the concentration of dust. When no dust is detected, the photosensitive detector outputs a low pulse; when the dust is detected, it outputs a high pulse, and the pulse signal is proportional to the detected light intensity.

Figure 2 The working principle of infrared LED light source
② Communication protocol
The infrared dust sensor can collect the value of the on-site concentration of dust in real time, and has two communication outputs of UART and PWM, which can meet the requirements of the concentration of dust monitoring system. The effective potential of the infrared dust sensor is low-level effective, and the potential judgment method of PM1006 is 4ms potential judgment. Its advantages are as follows:
• When the sensor keeps outputting a low level, the client can judge that the current test value of the sensor is 992ug/m3 through the high level of 4ms, rather than failure in the client device.
• When the sensor keeps outputting a high level, the client can judge that the current test value of the sensor is 0ug/m3 through the low level of 4ms, rather than failure in the client device.

Figure 3 PM1006 PWM communication protocol
③ Consistency and accuracy of detection under normal temperature environment
To verify the dust detection performance of the infrared dust sensor module PM1006, it is used to test 8mg of Hongtashan at an ambient temperature of 25±2°C and an ambient humidity of 50±10%RH. The test results show that the actual error of consistency error of PM1006 at room temperature is ±10%, and the accuracy error at room temperature meets the reading ±20ug/m3 or ±20%. Compared with ordinary infrared dust sensors, it has better consistency and accuracy.

Figure 4 Error Distribution of Normal Temperature Consistency of PM1006

Figure 5 Error distribution of room temperature accuracy of PM1006
4. Conclusion
Infrared dust sensor PM1006 has small sizes and low costs, and can be embedded in other household appliances or equipment that need to monitor air quality in real time, such as household air purifiers, air quality detectors, fresh air systems, air conditioners with purification functions, and accessories of consumer electronics, providing control signals for these instruments. The concentration of air dust in the environment can be calculated through the output of the infrared dust sensor. When the detected dust concentration is higher or lower than the set dust concentration threshold, the device is turned on or off to achieve the purpose of controlling the indoor concentration of dust.
Previous: The Application and Prospect of the Detection System
Next: Sensors




