On this page
An infrared sensor is a common electronic device used to detect and receive infrared radiation. They are widely used in remote control, security monitoring, thermal imaging and other fields. This article will introduce the working principle of infrared sensor and its different types.
The working principle of infrared sensors is based on the propagation of infrared radiation and its interaction with objects. Infrared radiation is a kind of electromagnetic wave with a long wavelength, which cannot be directly seen by the naked eye, but can be detected by specific infrared sensing equipment. When an object's temperature is above absolute zero (-273°C), it emits infrared radiation, and the intensity of the radiation is proportional to the temperature.
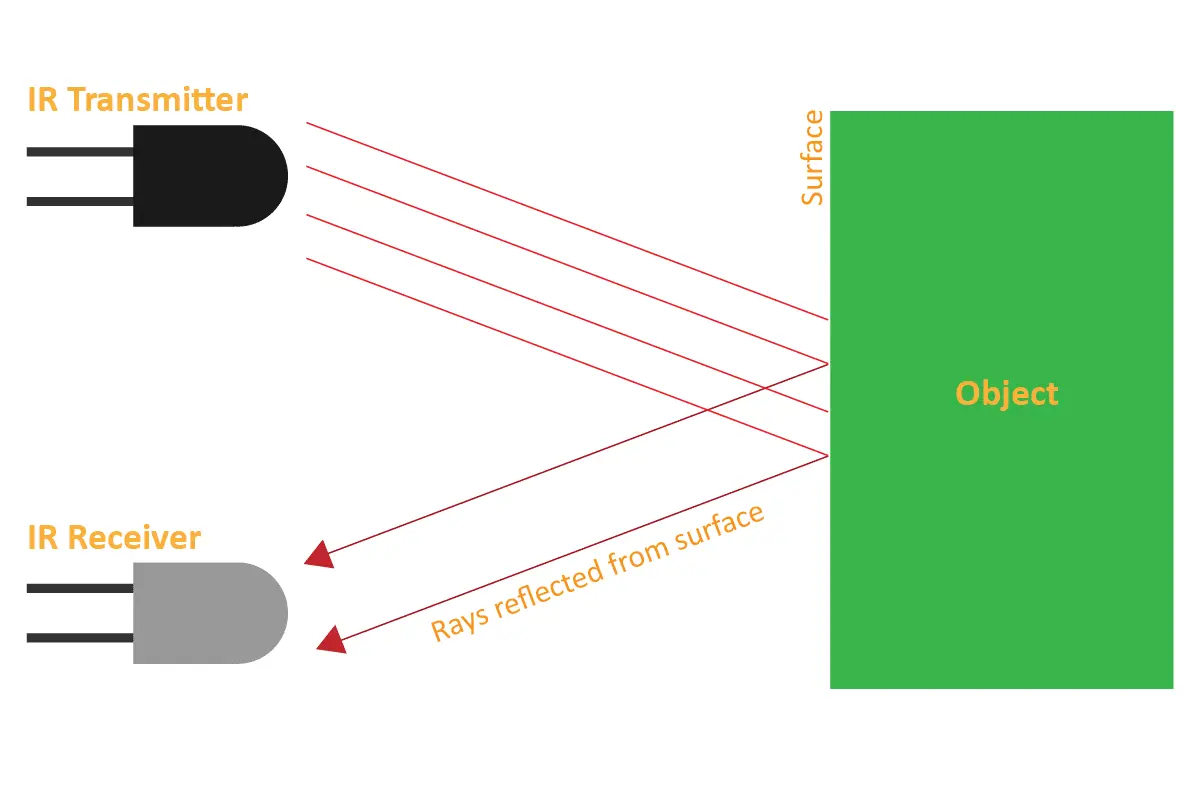
Infrared sensing equipment usually consists of a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter emits a specific wavelength of infrared light, and the receiver receives the radiation reflected back by the object. When the object approaches the sensing device, the infrared radiation detected by the receiver is enhanced. This is because the object absorbs some of the infrared light and reflects it back, causing the receiver to receive a stronger signal. This signal is then converted into an electrical signal and transmitted to the controller or alarm, which triggers the appropriate action.
 At a given temperature, the ratio of the radiant flux of any body to its absorption rate is constant and equal to the radiant flux of a blackbody at the same temperature. This means that the emissivity of the object is equal to the absorption rate, and the higher the absorption rate, the higher the emissivity. The intensity of thermal radiation of ground objects is proportional to the fourth power of temperature, so a small temperature difference will lead to significant changes in infrared radiation, which constitutes the theoretical basis of infrared remote sensing.
The total radiant flux of a blackbody increases rapidly with increasing temperature and is proportional to the fourth power of temperature. Therefore, a small change in temperature can lead to a large change in the radiation flux density, which is also the theoretical basis for infrared devices to measure temperature.
This law describes the relationship between the spectrum of blackbody radiation and temperature. As the temperature increases, the wavelength corresponding to the maximum radiation shifts to the shortwave direction.
According to different working principles and application requirements, infrared sensors can be divided into the following types:
The passive infrared sensor uses the working principle of thermistor and is mainly used for human detection and security monitoring. They detect the infrared radiation emitted by the human body to sense the presence of people, and are widely used in smart home and security systems.
Active infrared sensors detect by emitting infrared light themselves, usually consisting of infrared emitters and photodiodes, and are used in areas such as remote control, infrared communication and object detection.
An infrared thermal imaging camera is an advanced sensor capable of detecting the temperature distribution of an object's surface and generating a heat map. By capturing the infrared radiation emitted by the object, the thermal sensor or microarray technology is used to analyze the temperature difference and convert it into a visual image, which is widely used in the fields of thermal imaging, building inspection, medical diagnosis and military reconnaissance.
Infrared photodiodes consist of light-emitting diodes and photosensitive diodes, which are usually used for proximity detection and occlusion detection. They determine the presence or location of objects by measuring the blocking or reflection of infrared light and are widely used in automation control, manufacturing and robotics.
The infrared sensor is very sensitive to the detection of heat sources and can quickly capture temperature changes. This makes them highly valuable in the fields of fire warning, safety monitoring and non-destructive testing.
Infrared sensors can measure the temperature of an object at a certain distance without contact with the object. This feature enables them to ensure both measurement accuracy and user safety in harsh environments such as high temperature and high pressure.
Infrared sensors can perform real-time monitoring and provide real-time data. In areas such as industrial automation, smart homes and healthcare, real-time monitoring capabilities make infrared sensors an indispensable component.
Infrared sensors are small in size, light in weight, rich in interfaces, and easy to be integrated into various devices. Therefore, they are widely used in daily necessities such as smartphones and wearables to facilitate life.
Infrared sensors have excellent reliability in a variety of environments, are free from light interference, and can work stably in dark or strong light conditions.
Be affected by the environment
At a given temperature, the ratio of the radiant flux of any body to its absorption rate is constant and equal to the radiant flux of a blackbody at the same temperature. This means that the emissivity of the object is equal to the absorption rate, and the higher the absorption rate, the higher the emissivity. The intensity of thermal radiation of ground objects is proportional to the fourth power of temperature, so a small temperature difference will lead to significant changes in infrared radiation, which constitutes the theoretical basis of infrared remote sensing.
The total radiant flux of a blackbody increases rapidly with increasing temperature and is proportional to the fourth power of temperature. Therefore, a small change in temperature can lead to a large change in the radiation flux density, which is also the theoretical basis for infrared devices to measure temperature.
This law describes the relationship between the spectrum of blackbody radiation and temperature. As the temperature increases, the wavelength corresponding to the maximum radiation shifts to the shortwave direction.
According to different working principles and application requirements, infrared sensors can be divided into the following types:
The passive infrared sensor uses the working principle of thermistor and is mainly used for human detection and security monitoring. They detect the infrared radiation emitted by the human body to sense the presence of people, and are widely used in smart home and security systems.
Active infrared sensors detect by emitting infrared light themselves, usually consisting of infrared emitters and photodiodes, and are used in areas such as remote control, infrared communication and object detection.
An infrared thermal imaging camera is an advanced sensor capable of detecting the temperature distribution of an object's surface and generating a heat map. By capturing the infrared radiation emitted by the object, the thermal sensor or microarray technology is used to analyze the temperature difference and convert it into a visual image, which is widely used in the fields of thermal imaging, building inspection, medical diagnosis and military reconnaissance.
Infrared photodiodes consist of light-emitting diodes and photosensitive diodes, which are usually used for proximity detection and occlusion detection. They determine the presence or location of objects by measuring the blocking or reflection of infrared light and are widely used in automation control, manufacturing and robotics.
The infrared sensor is very sensitive to the detection of heat sources and can quickly capture temperature changes. This makes them highly valuable in the fields of fire warning, safety monitoring and non-destructive testing.
Infrared sensors can measure the temperature of an object at a certain distance without contact with the object. This feature enables them to ensure both measurement accuracy and user safety in harsh environments such as high temperature and high pressure.
Infrared sensors can perform real-time monitoring and provide real-time data. In areas such as industrial automation, smart homes and healthcare, real-time monitoring capabilities make infrared sensors an indispensable component.
Infrared sensors are small in size, light in weight, rich in interfaces, and easy to be integrated into various devices. Therefore, they are widely used in daily necessities such as smartphones and wearables to facilitate life.
Infrared sensors have excellent reliability in a variety of environments, are free from light interference, and can work stably in dark or strong light conditions.
Be affected by the environment
The measurement results of the infrared sensor may be affected by factors such as ambient temperature and humidity, resulting in errors. Therefore, environmental conditions need to be considered in the design and use process to ensure the accuracy of the measurement. The measurement distance of infrared sensors is usually limited, and the accuracy of long-distance detection may decline, which is not suitable for application scenarios that require long-distance measurement. Some high-precision infrared sensors, such as infrared thermal imaging sensors, are expensive and therefore may not have a price advantage in some applications. Because the infrared sensor is very sensitive to heat sources, it may be interfered with by other heat sources, resulting in inaccurate measurements. For example, in high temperature environments, the sensor may be false positive. The application range of infrared sensors is very wide, involving all walks of life. Here are a few main application areas:
 In industrial automation, infrared sensors are used to detect the presence, position and temperature of objects, which can help industrial equipment achieve contactless temperature measurement, thereby improving production efficiency and product quality.
In the field of security monitoring, infrared sensors are used to detect infrared radiation from intruders to achieve monitoring at night or under low light conditions. They are also widely used in fire warning systems to send alarms in time by detecting thermal radiation from fire sources.
Infrared sensors are also widely used in medical devices, such as thermometers, oximeters and heart rate monitors, to help monitor the body's temperature and physiological signals.
In smart homes, infrared sensors are often used for lighting control, air conditioning and security systems. They can automatically sense the presence of the human body, thereby controlling the switch of the device, providing users with a convenient and energy-saving life experience.
In the field of automotive electronics, infrared sensors are widely used in night vision systems, autonomous driving systems and collision warning systems, which can detect the road and obstacles ahead in dark or bad weather conditions to improve driving safety.
Infrared sensors are also used for environmental monitoring, such as detecting greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, monitoring volcanic activity and forewarning forest fires. By detecting infrared radiation, infrared sensors can help scientists better understand and respond to environmental changes.
In short, infrared sensors, with their advantages of high sensitivity, non-contact measurement, real-time monitoring, easy integration and high reliability, have been widely used in industrial automation, security monitoring, medical equipment, smart home, automotive electronics and environmental monitoring. However, they also face challenges such as environmental impacts, limited measurement distances, higher costs and susceptibility to interference. In the future, with the continuous development of technology, infrared sensors will continue to make breakthroughs in miniaturization, intelligence, multi-function, high precision and low power consumption, providing support and guarantee for more applications in more fields.
In industrial automation, infrared sensors are used to detect the presence, position and temperature of objects, which can help industrial equipment achieve contactless temperature measurement, thereby improving production efficiency and product quality.
In the field of security monitoring, infrared sensors are used to detect infrared radiation from intruders to achieve monitoring at night or under low light conditions. They are also widely used in fire warning systems to send alarms in time by detecting thermal radiation from fire sources.
Infrared sensors are also widely used in medical devices, such as thermometers, oximeters and heart rate monitors, to help monitor the body's temperature and physiological signals.
In smart homes, infrared sensors are often used for lighting control, air conditioning and security systems. They can automatically sense the presence of the human body, thereby controlling the switch of the device, providing users with a convenient and energy-saving life experience.
In the field of automotive electronics, infrared sensors are widely used in night vision systems, autonomous driving systems and collision warning systems, which can detect the road and obstacles ahead in dark or bad weather conditions to improve driving safety.
Infrared sensors are also used for environmental monitoring, such as detecting greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, monitoring volcanic activity and forewarning forest fires. By detecting infrared radiation, infrared sensors can help scientists better understand and respond to environmental changes.
In short, infrared sensors, with their advantages of high sensitivity, non-contact measurement, real-time monitoring, easy integration and high reliability, have been widely used in industrial automation, security monitoring, medical equipment, smart home, automotive electronics and environmental monitoring. However, they also face challenges such as environmental impacts, limited measurement distances, higher costs and susceptibility to interference. In the future, with the continuous development of technology, infrared sensors will continue to make breakthroughs in miniaturization, intelligence, multi-function, high precision and low power consumption, providing support and guarantee for more applications in more fields.
Infrared sensing equipment usually consists of a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter emits a specific wavelength of infrared light, and the receiver receives the radiation reflected back by the object. When the object approaches the sensing device, the infrared radiation detected by the receiver is enhanced. This is because the object absorbs some of the infrared light and reflects it back, causing the receiver to receive a stronger signal. This signal is then converted into an electrical signal and transmitted to the controller or alarm, which triggers the appropriate action.
 At a given temperature, the ratio of the radiant flux of any body to its absorption rate is constant and equal to the radiant flux of a blackbody at the same temperature. This means that the emissivity of the object is equal to the absorption rate, and the higher the absorption rate, the higher the emissivity. The intensity of thermal radiation of ground objects is proportional to the fourth power of temperature, so a small temperature difference will lead to significant changes in infrared radiation, which constitutes the theoretical basis of infrared remote sensing.
The total radiant flux of a blackbody increases rapidly with increasing temperature and is proportional to the fourth power of temperature. Therefore, a small change in temperature can lead to a large change in the radiation flux density, which is also the theoretical basis for infrared devices to measure temperature.
This law describes the relationship between the spectrum of blackbody radiation and temperature. As the temperature increases, the wavelength corresponding to the maximum radiation shifts to the shortwave direction.
According to different working principles and application requirements, infrared sensors can be divided into the following types:
The passive infrared sensor uses the working principle of thermistor and is mainly used for human detection and security monitoring. They detect the infrared radiation emitted by the human body to sense the presence of people, and are widely used in smart home and security systems.
Active infrared sensors detect by emitting infrared light themselves, usually consisting of infrared emitters and photodiodes, and are used in areas such as remote control, infrared communication and object detection.
An infrared thermal imaging camera is an advanced sensor capable of detecting the temperature distribution of an object's surface and generating a heat map. By capturing the infrared radiation emitted by the object, the thermal sensor or microarray technology is used to analyze the temperature difference and convert it into a visual image, which is widely used in the fields of thermal imaging, building inspection, medical diagnosis and military reconnaissance.
Infrared photodiodes consist of light-emitting diodes and photosensitive diodes, which are usually used for proximity detection and occlusion detection. They determine the presence or location of objects by measuring the blocking or reflection of infrared light and are widely used in automation control, manufacturing and robotics.
The infrared sensor is very sensitive to the detection of heat sources and can quickly capture temperature changes. This makes them highly valuable in the fields of fire warning, safety monitoring and non-destructive testing.
Infrared sensors can measure the temperature of an object at a certain distance without contact with the object. This feature enables them to ensure both measurement accuracy and user safety in harsh environments such as high temperature and high pressure.
Infrared sensors can perform real-time monitoring and provide real-time data. In areas such as industrial automation, smart homes and healthcare, real-time monitoring capabilities make infrared sensors an indispensable component.
Infrared sensors are small in size, light in weight, rich in interfaces, and easy to be integrated into various devices. Therefore, they are widely used in daily necessities such as smartphones and wearables to facilitate life.
Infrared sensors have excellent reliability in a variety of environments, are free from light interference, and can work stably in dark or strong light conditions.
Be affected by the environment
At a given temperature, the ratio of the radiant flux of any body to its absorption rate is constant and equal to the radiant flux of a blackbody at the same temperature. This means that the emissivity of the object is equal to the absorption rate, and the higher the absorption rate, the higher the emissivity. The intensity of thermal radiation of ground objects is proportional to the fourth power of temperature, so a small temperature difference will lead to significant changes in infrared radiation, which constitutes the theoretical basis of infrared remote sensing.
The total radiant flux of a blackbody increases rapidly with increasing temperature and is proportional to the fourth power of temperature. Therefore, a small change in temperature can lead to a large change in the radiation flux density, which is also the theoretical basis for infrared devices to measure temperature.
This law describes the relationship between the spectrum of blackbody radiation and temperature. As the temperature increases, the wavelength corresponding to the maximum radiation shifts to the shortwave direction.
According to different working principles and application requirements, infrared sensors can be divided into the following types:
The passive infrared sensor uses the working principle of thermistor and is mainly used for human detection and security monitoring. They detect the infrared radiation emitted by the human body to sense the presence of people, and are widely used in smart home and security systems.
Active infrared sensors detect by emitting infrared light themselves, usually consisting of infrared emitters and photodiodes, and are used in areas such as remote control, infrared communication and object detection.
An infrared thermal imaging camera is an advanced sensor capable of detecting the temperature distribution of an object's surface and generating a heat map. By capturing the infrared radiation emitted by the object, the thermal sensor or microarray technology is used to analyze the temperature difference and convert it into a visual image, which is widely used in the fields of thermal imaging, building inspection, medical diagnosis and military reconnaissance.
Infrared photodiodes consist of light-emitting diodes and photosensitive diodes, which are usually used for proximity detection and occlusion detection. They determine the presence or location of objects by measuring the blocking or reflection of infrared light and are widely used in automation control, manufacturing and robotics.
The infrared sensor is very sensitive to the detection of heat sources and can quickly capture temperature changes. This makes them highly valuable in the fields of fire warning, safety monitoring and non-destructive testing.
Infrared sensors can measure the temperature of an object at a certain distance without contact with the object. This feature enables them to ensure both measurement accuracy and user safety in harsh environments such as high temperature and high pressure.
Infrared sensors can perform real-time monitoring and provide real-time data. In areas such as industrial automation, smart homes and healthcare, real-time monitoring capabilities make infrared sensors an indispensable component.
Infrared sensors are small in size, light in weight, rich in interfaces, and easy to be integrated into various devices. Therefore, they are widely used in daily necessities such as smartphones and wearables to facilitate life.
Infrared sensors have excellent reliability in a variety of environments, are free from light interference, and can work stably in dark or strong light conditions.
Be affected by the environmentThe measurement results of the infrared sensor may be affected by factors such as ambient temperature and humidity, resulting in errors. Therefore, environmental conditions need to be considered in the design and use process to ensure the accuracy of the measurement. The measurement distance of infrared sensors is usually limited, and the accuracy of long-distance detection may decline, which is not suitable for application scenarios that require long-distance measurement. Some high-precision infrared sensors, such as infrared thermal imaging sensors, are expensive and therefore may not have a price advantage in some applications. Because the infrared sensor is very sensitive to heat sources, it may be interfered with by other heat sources, resulting in inaccurate measurements. For example, in high temperature environments, the sensor may be false positive. The application range of infrared sensors is very wide, involving all walks of life. Here are a few main application areas:
 In industrial automation, infrared sensors are used to detect the presence, position and temperature of objects, which can help industrial equipment achieve contactless temperature measurement, thereby improving production efficiency and product quality.
In the field of security monitoring, infrared sensors are used to detect infrared radiation from intruders to achieve monitoring at night or under low light conditions. They are also widely used in fire warning systems to send alarms in time by detecting thermal radiation from fire sources.
Infrared sensors are also widely used in medical devices, such as thermometers, oximeters and heart rate monitors, to help monitor the body's temperature and physiological signals.
In smart homes, infrared sensors are often used for lighting control, air conditioning and security systems. They can automatically sense the presence of the human body, thereby controlling the switch of the device, providing users with a convenient and energy-saving life experience.
In the field of automotive electronics, infrared sensors are widely used in night vision systems, autonomous driving systems and collision warning systems, which can detect the road and obstacles ahead in dark or bad weather conditions to improve driving safety.
Infrared sensors are also used for environmental monitoring, such as detecting greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, monitoring volcanic activity and forewarning forest fires. By detecting infrared radiation, infrared sensors can help scientists better understand and respond to environmental changes.
In short, infrared sensors, with their advantages of high sensitivity, non-contact measurement, real-time monitoring, easy integration and high reliability, have been widely used in industrial automation, security monitoring, medical equipment, smart home, automotive electronics and environmental monitoring. However, they also face challenges such as environmental impacts, limited measurement distances, higher costs and susceptibility to interference. In the future, with the continuous development of technology, infrared sensors will continue to make breakthroughs in miniaturization, intelligence, multi-function, high precision and low power consumption, providing support and guarantee for more applications in more fields.
In industrial automation, infrared sensors are used to detect the presence, position and temperature of objects, which can help industrial equipment achieve contactless temperature measurement, thereby improving production efficiency and product quality.
In the field of security monitoring, infrared sensors are used to detect infrared radiation from intruders to achieve monitoring at night or under low light conditions. They are also widely used in fire warning systems to send alarms in time by detecting thermal radiation from fire sources.
Infrared sensors are also widely used in medical devices, such as thermometers, oximeters and heart rate monitors, to help monitor the body's temperature and physiological signals.
In smart homes, infrared sensors are often used for lighting control, air conditioning and security systems. They can automatically sense the presence of the human body, thereby controlling the switch of the device, providing users with a convenient and energy-saving life experience.
In the field of automotive electronics, infrared sensors are widely used in night vision systems, autonomous driving systems and collision warning systems, which can detect the road and obstacles ahead in dark or bad weather conditions to improve driving safety.
Infrared sensors are also used for environmental monitoring, such as detecting greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, monitoring volcanic activity and forewarning forest fires. By detecting infrared radiation, infrared sensors can help scientists better understand and respond to environmental changes.
In short, infrared sensors, with their advantages of high sensitivity, non-contact measurement, real-time monitoring, easy integration and high reliability, have been widely used in industrial automation, security monitoring, medical equipment, smart home, automotive electronics and environmental monitoring. However, they also face challenges such as environmental impacts, limited measurement distances, higher costs and susceptibility to interference. In the future, with the continuous development of technology, infrared sensors will continue to make breakthroughs in miniaturization, intelligence, multi-function, high precision and low power consumption, providing support and guarantee for more applications in more fields.Previous: Precautions for Installing CO2 Monitoring Systems
Next: One Factor Affecting the Reading of the Gas Sensor: Gas Concentration





